Implementation Plan (1987)
Planning agency: International Highway Construction Corporation
Implementing agency: Kyokuto Kaihatsu Co., Ltd.
Underwater geological survey area 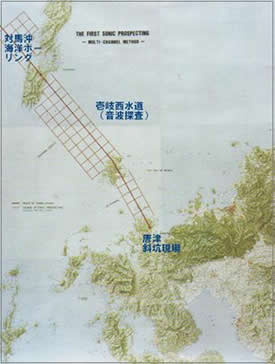 along the Japan-Korea tunnel route
along the Japan-Korea tunnel route
This survey was planned to include a single-channel sonic survey using a sparker and a seafloor geological survey using a side-scan sonar.
The basic route for the Japan-Korea tunnel is considered to be promising, starting from Higashimatsuura Peninsula in Saga Prefecture in Kyushu, passing through Iki Island, entering the southern part of Tsushima Island (Shimojima), and then going from near Gosaki on the west side to Geoje Island on the Korean side. ing. The submarine topography and geological survey of the marine area along this route began with multi-channel sonic survey using a Sparker in 1983, single-channel sonic survey and bathymetric survey using a Sparker, multi-channel sonic survey using a water gun, dredging equipment, Ocean boring and other activities were carried out, and many submarine topography and geological maps were obtained. This time, we will carry out a geological survey of the seabed topography in the waters north of the Tsushima West Channel, which will serve as basic information for route selection.
① Survey of seafloor topography using acoustic bathymetry
② Survey of seabed geology and geological structure using sparker single channel sonic survey
③ Survey of seafloor topography and bottom sediment using side scan sonic imaging device
④ Measurement of tide level using tide gauge
① Acoustic sounding: 1,160km
② Sparker single channel sonic survey: 810km
③ Side scan sonic imaging: 350km
④ Tide measurement: Measured every 10 minutes during work
The survey period is from May 1st to July 31st, 1988.
1.
Ship position measurement The ship position is measured using the two-distance intersection method using a radio positioning device (tryponder).
The slave point uses a known reference point. Four slave stations are used, and two stations suitable for ship position measurement are selected at any time so that the angle of intersection between the two distances falls within the range of 30° to 150°. Data is output from a printer using an X-Y converter and input to magnetic tape. The virtual origin of the exchange coordinate system used this time to improve work efficiency was set to the
first system X=152490.0 Y=-12191.3 θ=320.0°.

*Sonic wave exploration using a sparker as a sound source
2.
acoustic sounding machine (PDR-101 type).
A fixed line is inserted every two minutes to ensure correspondence with the wake. Bar checks should be performed once a day or every time recording paper, pens, etc. are replaced.
Measurements are taken twice, once every 5 meters until the depth reaches 50 meters, ``lowering'' and ``raising''. For depths deeper than 50m, calculations are made from revised curves obtained from data such as seawater temperature, pressure, and salinity. Adjust stuttering according to changes in stuttering.
3.
sonic exploration sparker as the sound source. This energy source can be used from 200 to 8000 joules. Prior to the survey, a test run will be conducted to determine the ship speed, magnitude of seismic energy, towing length of the spark array and hydrohorn, depth, filter bandwidth, etc., and initial conditions suitable for the survey will be set.
4.
Acoustic imaging seafloor topography and geological survey Conducting a seafloor acoustic imaging survey using site scan sonar. A fan-shaped sound wave of 100KHz/500KHz is oscillated from inside the towfish, which is towed from the stern of the ship, onto the ocean floor. After receiving reflected waves from the seabed and converting them into electrical signals, they perform slope distance correction, amplitude correction, ship speed correction, and output on recording paper. The data will also be recorded.
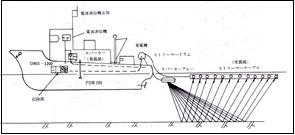
*Outline diagram of the rigging of the research vessel
5.
the tide survey period, tide records from Sasuna, Kamigata Town, Tsushima will be used.
If the survey is to be carried out in a location without a tidal station, select an appropriate observation location and directly observe the tide height to the nearest 1 cm every 10 minutes on a scale. Perform leveling of the waterway basic level markers and observation locations, and calculate the basic level surface. This is used as the water depth correction value for acoustic sounding.
6. Deliverables
Investigation report (overview)
construction survey of Japan-Korea tunnel
construction survey of Japan-Korea tunnel
Overview of the Japan-Korea tunnel