Efforts should be made to promote the use of soil generated by excavation during shield construction as a recycled resource.
Excavated soil is a construction by-product, and in accordance with the Recycling Law (1991), efforts must be made to reuse it as a resource as much as possible.
There are several ways to utilize waste construction sludge:
1. Use it yourself
2. Sell it for a fee
3. Use the recycling system (recycling designation system, recycling certification system)
Construction sludge may be subjected to intermediate treatment to be recycled in order to reduce waste and protect the environment. In this case, it is necessary to test for the content of hazardous substances and perform intermediate treatment according to the quality specified for the material, the required shape, etc., and the shield construction equipment.
When intermediate treatment is carried out, the most appropriate treatment method must be selected taking into consideration the soil conditions, the method of transportation inside the mine, the method of transportation through the shaft, the size of the shaft site, the conditions of the disposal site, etc., and procedures must be followed for equipment such as dehydration treatment facilities with the necessary treatment capacity to be notified to local governments.
The soil generated by shield construction must be properly treated and disposed of.
Of the materials discharged during shield construction, muddy material with a high water content and fine particles is treated as inorganic sludge. Such waste sludge must be properly treated and disposed of in accordance with the Waste Disposal Act. Generally, a muddy state refers to a state in which it cannot be piled up in a standard dump truck and people cannot walk on it. In terms of soil strength indicators, this state corresponds to a cone index of approximately 200 kN/m2 or less, or an unconfined compressive strength of approximately 50 kN/m2 or less.
If a contractor disposes of waste themselves, they must comply with the disposal standards stipulated in the Waste Management and Public Cleansing Act. If they outsource disposal, they must also comply with the outsourcing standards, such as confirming that the contractor has an industrial waste disposal license, entering into a written outsourcing contract, and issuing an industrial waste management form (manifest).
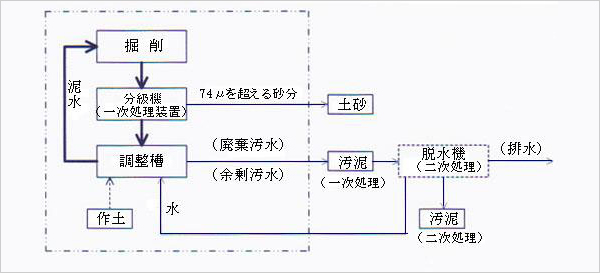
*Examples of muddy water circulation methods
(muddy water shield method, reverse circulation method)
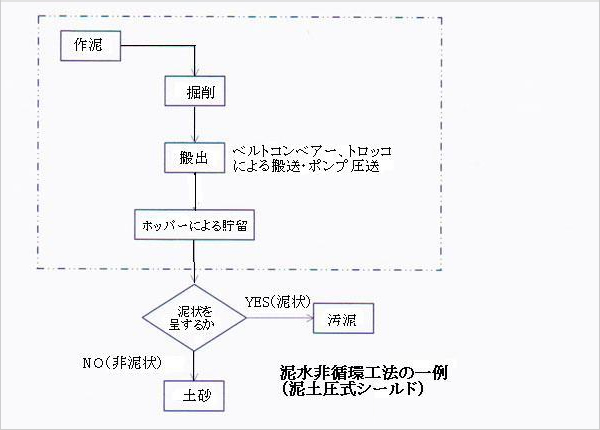
(Reference: "Tunnel Standard Specifications - Shield Method, Established in 2006," Japan Society of Civil Engineers)
Environmental assessment
(environmental impact assessment)
Overview of the Japan-Korea Tunnel